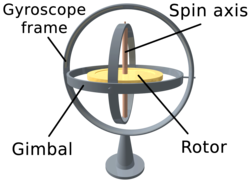
Gyroscope
A gyroscope (from Greek γῦρος gûros, "circle" and σκοπέω skopéō, "to look") is a spinning wheel or disc in which the axis of rotation is free to assume any orientation by itself. When rotating, the orientation of this axis is unaffected by tilting or rotation of the mounting, according to the conservation of angular momentum. Because of this, gyroscopes are useful for measuring or maintaining orientation.[1][2]
Gyroscopes based on other operating principles also exist, such as the electronic, microchip-packaged MEMS gyroscopes found in consumer electronics devices, solid-state ring lasers, fibre optic gyroscopes, and the extremely sensitive quantum gyroscope.[citation needed]
Applications of gyroscopes include inertial navigation systems where magnetic compasses would not work (as in theHubble telescope) or would not be precise enough (as in intercontinental ballistic missiles), or for the stabilization of flying vehicles like radio-controlled helicopters or unmanned aerial vehicles, and recreational boats and commercial ships. Due to their precision, gyroscopes are also used in gyrotheodolites to maintain direction in tunnel mining.[3]Gyroscopes can be used to construct gyrocompasses, which complement or replace magnetic compasses (in ships, aircraft and spacecraft, vehicles in general), to assist in stability (Hubble Space Telescope, bicycles, motorcycles, and ships) or be used as part of an inertial guidance system.
Modern uses
In addition to being used in compasses, aircraft, computer pointing devices, etc., gyroscopes have been introduced into consumer electronics. Since the gyroscope allows the calculation of orientation and rotation, designers have incorporated them into modern technology. The integration of the gyroscope has allowed for more accurate recognition of movement within a 3D space than the previous lone accelerometer within a number of smartphones. Gyroscopes in consumer electronics are frequently combined with accelerometers (acceleration sensors) for more robust direction- and motion-sensing. Examples of such applications include smartphones such as the Samsung Galaxy Note 4,[46] HTC Titan,[47] Nexus 5,iPhone 5s,[48] Nokia 808 PureView[49] and Sony Xperia, game console peripherals such as the PlayStation 3 controller and the Wii Remote, and virtual reality sets such as the Oculus Rift.[50][not in citation given]
Nintendo has integrated a gyroscope into the Wii console's Wii Remote controller by an additional piece of hardware called "Wii MotionPlus".[51] It is also included in the 3DS and the Wii U GamePad, which detects movement when turning.
Cruise ships use gyroscopes to level motion-sensitive devices such as self-leveling pool tables.
An electric powered flywheel gyroscope inserted in a bicycle wheel is being sold as a training wheel alternative.